British India to 1857: The Rise and Fall of the East India Company
If you follow me on Twitter or read last week’s blog post, you’ll know I’m just back from a holiday in India. I’d like to blog about India while the country is still top of my mind. Last week I did touch on how the war of 1857 (the Indian Mutiny or the First War of Independence depending on when and where you learned about it) still affects the way Indians view their history and their relationship with Britain, although not as much as you might expect. I thought that this week I’d take a look at the events that led up to the War of 1857. I’ve covered this before and my post about it remains one of the most widely read I’ve ever done, so it seems worth repeating for an audience that might not have been following me back when I wrote it.
#############################
In the mid-19th century, India, the jewel in Britain’s imperial crown wasn’t, technically, part of the Empire at all. It was run by the East India Company, a commercial organisation, originally set up to trade with the Far East. Under the India Act of 1784, the activities of the Company were subject to direction from the British government, but the Company remained a commercial organisation with shareholders who were paid dividends from the Company’s substantial profits. How had we reached a situation where one of the world’s largest countries was being administered for profit by a private company?
For centuries, Europe had traded with the Far East. The spice trade was of vital economic importance as far back as the days of Ancient Rome. Look in your store cupboard, even today, and see how many of the spices we use come from the Far East. And remember that, in the days before refrigeration, spices were essential in making meat palatable.
Until the 15th century, trade routes to the East went overland and were controlled first by Arabs and later by the Ottoman Turks. It was not until 1498 that the Portuguese explorer, Vasco da Gama, navigated round the Cape of Good Hope and opened a sea route from Europe to the Far East. This meant that European merchants could trade directly with their suppliers and a new age of maritime commerce was born.
Britain was late to the party. By the time that the Queen Elizabeth signed the original Royal Charter of the East India Company in 1600, the Portuguese and the Dutch were well established in the Far East. Repeatedly rebuffed by their rivals in the East Indies, Britain looked to the possibilities of India.
It was not until 1639 that the Company established its first permanent base in India, in Madras on the Bay of Bengal. In 1668, it acquired Bombay, and then Calcutta followed in 1690. These three “factories”, as they were known, were intended as trading outposts: places where merchants could warehouse goods imported and exported in the increasingly profitable trade between Britain and the Indian states.
By the 1740s, the main threat in India came not from the Portuguese or the Dutch, but from the French. Their principal trading point was at Pondicherry, less than 100 miles from Madras. In 1749, the local ruler died. There were two rival claimants for his throne. The French and the British, both trying to extend their own influence, each backed one of the rivals. Both trading companies had their own military forces to defend their activities and each supported their own choice for ruler with troops. Open war was underway by 1750.
Although the dispute was notionally between two Indian princes, involvement of French and British trading companies led, inexorably, to the involvement of the French and British governments. Both sides sent professional government troops to support their own trading companies.
Backed by the military and naval resources of Britain and France, the two companies had now become significant political forces in the region. At this point, in 1756, a separate war broke out a thousand miles away, where the nawab of Bengal attacked and occupied Calcutta. The military build-up around Madras meant that the British were in a position to respond decisively. Ships of the Royal Navy carried an army from Madras to Bengal. At the Battle of Plassey on 23 June 1757, Robert Clive, commanding the forces of the East India Company decisively defeated the Nawab of Bengal, supported by French troops. The defeat of the Nawab was of huge symbolic importance and Plassey came to be seen as marking the start of British rule in India.

Statue of Clive of India. Whitehall, London
Immediately following the victory at Plassey, Clive installed the British candidate, Mir Jafar, as Nawab of Bengal, Orissa and Bihar. Effectively, the East India Company now governed Bengal through a puppet ruler.
The tax revenues of these provinces now passed to the Company with Mir Jafar left responsible for justice and policing. (The Company took over even these residual powers in 1772.) All Frenchmen were expelled from Bengal. With the revenue from Bengal, the company was able to expand its efforts against the French further south and their hold over Pondicherry was destroyed in 1761.
India, at this time, was not a single country. The place was governed by local rulers, some with limited authority while some were absolute monarchs of huge areas of the subcontinent. All, though, recognised that the political and military presence of the British had changed the balance of power for ever. Some chose to make formal alliances with the British. Others sought to maintain some kind of independence by joining with the French.
The Sultan of Mysore allied with them to war on the Company in southern India in the late 1770s and 80s. His son, Tipu, became the most powerful threat to British hegemony. He styled himself the “Tiger of Mysore” with tiger motifs worked into his uniforms, cannons, cane handles, bed hangings, swords and thrones. His famous model of a full size tiger killing an East India Company soldier is now on display in London’s Victoria & Albert Museum.

Tipu Sultan sent agents to Europe to buy arms that might enable him to meet the British on equal terms. Intelligence reports suggested he bought 50 cannon, 80 gun carriages, and 100,000 cannonballs, besides muskets and sabres. His army was built up to the point where he did pose a real threat to the British, but he was ultimately defeated, dying in battle in 1799.
By now, the Company was committed to Indian politics. Company troops had to defend the borders of those rulers that the Company had put in power and this meant coming to terms with their neighbours. In some cases “coming to terms” meant crushing militarily. In others, alliances were formed. The continuing involvement of the French, trying to regain territories that they had lost, and carrying on their Revolutionary Wars in the Indian theatre, meant that the Company continually felt under threat. Rulers who had not been won over to the British side might always ally with the French. Every new territorial gain, therefore, meant more territory that had to be defended, which, in turn, meant the need for further expansion.
The British conquest of India, state by state, was far from being motivated solely by the need for self-defence. The settlement after Plassey, gave the East India Company vast tax revenues. Clive predicted a £2 million annual revenue surplus (an incredible sum in 1760), which led to a 100% rise in the price of Company stock.
The military also benefited directly from the campaigns that accompanied the Company’s expansion. The word “loot” comes from the Hindu word for booty and its adoption into the English language gives an indication of the enthusiasm with which European troops plundered their enemies. Everyone from the humblest private to the general could expect to get rich should they survive a war in India.
As the Company moved from a commercial to a political entity, trade became an increasingly unimportant part of its activities. In 1833 the Charter Act ended the Company’s trading rights in India, as trading was deemed to be incompatible with ruling. The East India Company was therefore the ultimate example of privatisation. The entire government of one of the largest countries in the world had been outsourced to a private supplier whose profits came from the tax surplus of the nation that they governed. (Thomas Babington Macaulay, a leading British politician who served on the Supreme Council of India, described it as “the strangest of all governments … designed for the strangest of all empires”.)
Government for profit clearly had a vast potential for abuse. A clear example of this came early in the East India Company’s rule, with the Bengal Famine of 1770. This is estimated to have killed around 10 million people – about a quarter of the population of the province. During this time, the government of the East India Company took no effective measures to reduce starvation but, instead, increased land taxes and encouraged the growing of non-food crops (including opium) instead of the desperately needed rice.
Despite horrors such as the famine, many aspects of British rule were benign. In a time when communications with India were slow, British administrators would spend years in post, often not returning to Britain for long periods. In general, the late 18th century saw a relaxed coexistence between the Company’s servants and the native rulers. Many pleasures were shared, with British officers often enjoying lavish hospitality from native rulers.
Initially too, intermarriage was encouraged, with the Company giving cash gifts when their employees had children with Indian women, on the basis that the children would grow up to soldier for the Company. Colonel James Skinner, the founder of a famous cavalry troop, Skinner’s Horse, fathered a substantial Anglo-Indian dynasty. According to his family he had seven wives, while legend claims he had fourteen. In appropriately multi-denominational style, Skinner built a mosque for one Muslim wife, a temple for a Hindu one and then his own church in Delhi, where he was buried in 1841.
The result of such good relationships was a European ruling class that, for a while at least, demonstrated some understanding of India and a real interest in improving the economy of the country. The commitment of enlightened European rulers to their Indian subjects was rewarded with a surprising degree of loyalty and respect by many of the Indians.
By the mid-19th century, though, such mutual respect and understanding was breaking down. One in three wills made by Company servants between 1780 and 1785 made provision for Indian wives or mistresses. Between 1805 and 1810, it was down to one in four and by the middle of the century, such provisions had almost entirely disappeared. A new breed of administrators was ruling India, often contemptuous of all things native. Christian missionaries, whose activities had been restricted by the Company until 1833, were now proselytising widely in a country which was not naturally inclined to Christianity. Changes in the structure of the Army had reduced the pay and promotion opportunities of native soldiers. Perhaps most seriously, the British now controlled so much of India that they were increasingly ruthless in their manipulation of the law in order to seize those few states that remained even notionally independent.
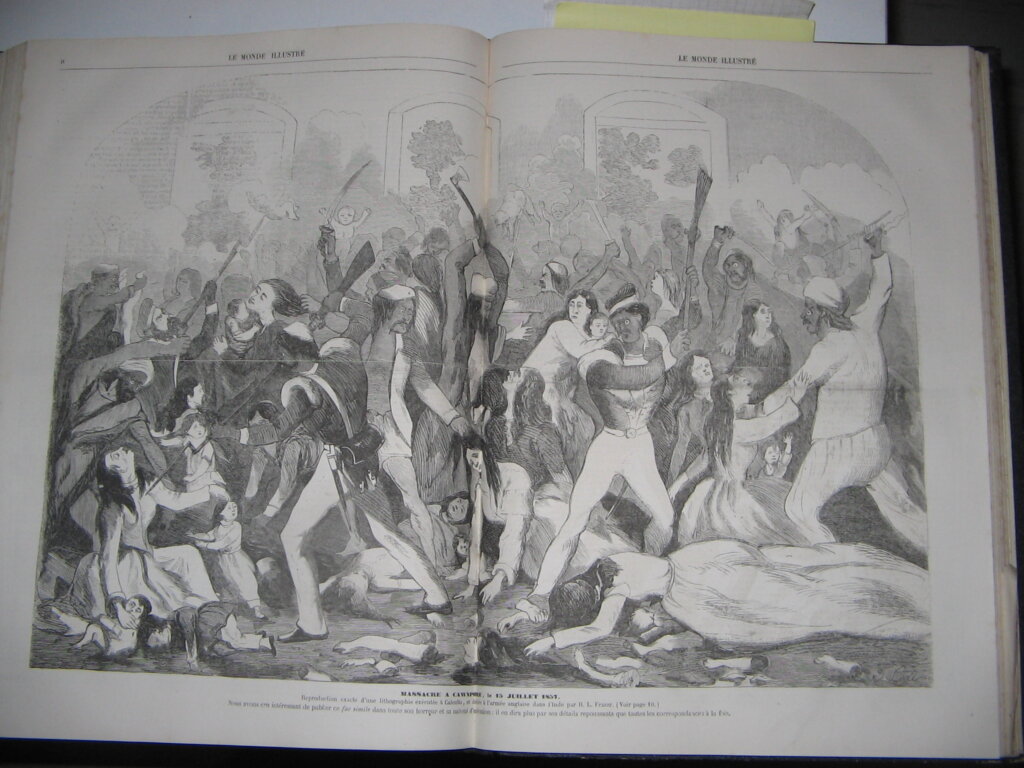
By the time of my novel, Cawnpore, British rule had lasted almost 100 years. A trading company, still structured as a commercial organisation, was ruling over around 200 million people. It was a time of technological and social change, yet the administration was increasingly out of touch with the people and the army was restless. The scene was set for revolution.
In 1857 a rumour spread that the cartridges issued to native troops had been greased with pig and beef fat, making them unclean for both Moslems and Hindus. The story about the fat may well have been untrue. Despite official inquiries, no one will ever know for sure. On 24th April Colonel Carmichael-Smyth of the 3rd Light Cavalry took it on himself (against the advice of many of his officers) to insist that his men drill with the new cartridges. The men refused and 85 were convicted of mutiny. On May 9th, the men were paraded in chains before their regiment at Meerut in north west India and marched off to jail. Shamed by the treatment of their comrades, the regiment rose in revolt on Sunday 10th May, 1857. The Indian Mutiny had begun.
What started as a mutiny in one small outpost became a revolt that swept across the sub-continent and nearly saw Britain driven from its most important colonial possession. When it was over, millions had died, either in the fighting or the reprisals that followed. The East India Company was abolished soon afterwards. The British continued to rule for almost another hundred years, but the relationship between rulers and ruled had changed forever.
Cawnpore

My book, Cawnpore, is set around the siege of Cawnpore, which was a particularly terrible incident in a particularly horrible war. It’s my personal favourite of all the books I’ve written. It’s the second of my books to feature John Williamson, but it’s completely self-contained, so you don’t have to read The White Rajah first. It’s available as an e-book or in paperback.
Cawnpore has not got anything like the sales of my James Burke books, which I think is a pity because people have said some very nice things about it:
“For anyone who has a love for this period, Cawnpore is probably one for you.” Historical Novel Society
“All that historical fiction should be: absorbing, believable and educational.” – Terry Tyler in Terry Tyler Book Reviews
The Kindle edition is an absurdly inexpensive £3.99. Please buy it.
The photo at the top of this post shows part of the royal palace within Delhi’s Red Fort.